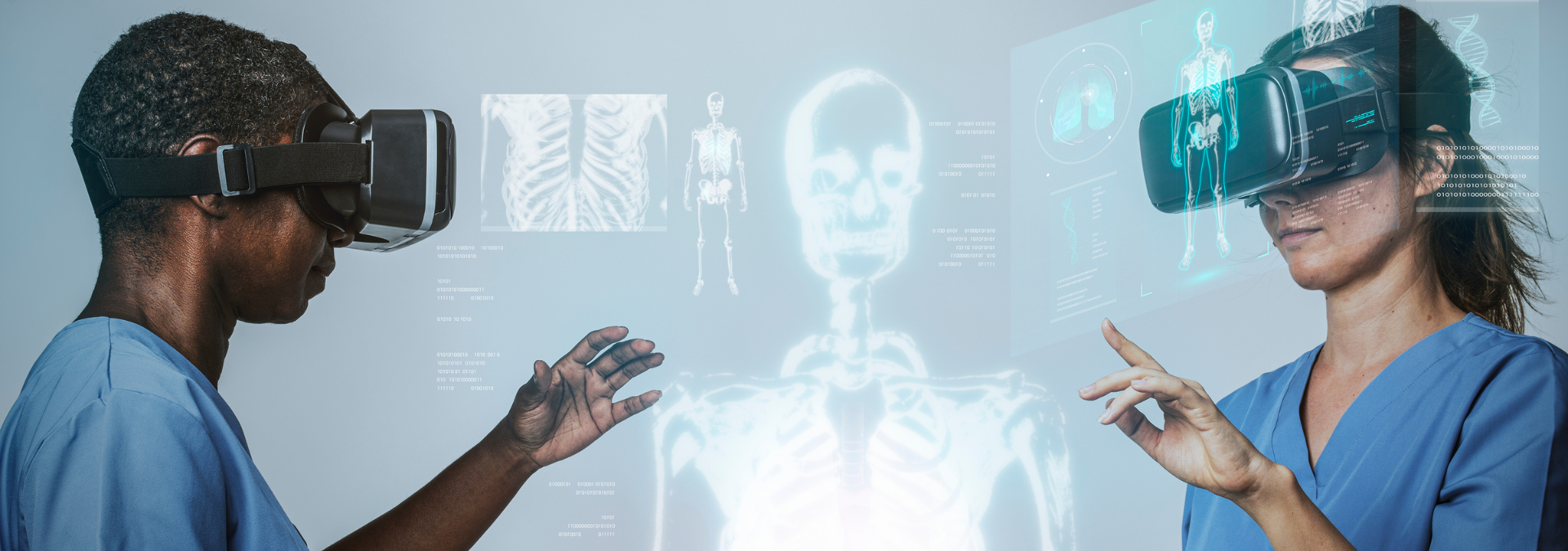
The effects of augmented reality in healthcare are being felt right before our eyes. During a surgical procedure, a surgeon can review patient vitals via an augmented reality (AR) equipped head-mounted device instead of switching between several devices and screens. If they do this, there will be less room for error in their interpretation of the data.
Improve healthcare delivery and the patient experience using head-mounted displays, wearables, and mobile applications that enable interactions between the real environment and virtual items. Like how artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics (DA) have benefited your caregiving organization, augmented reality (AR) offers promising new avenues for improvement for practitioners, payers, and manufacturers of medical technology.
Soon there will be no way around augmented reality if one wants to boost the productivity, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Given a choice between augmenting existing business processes and investing extensively in enabling new processes, who would not choose the former?
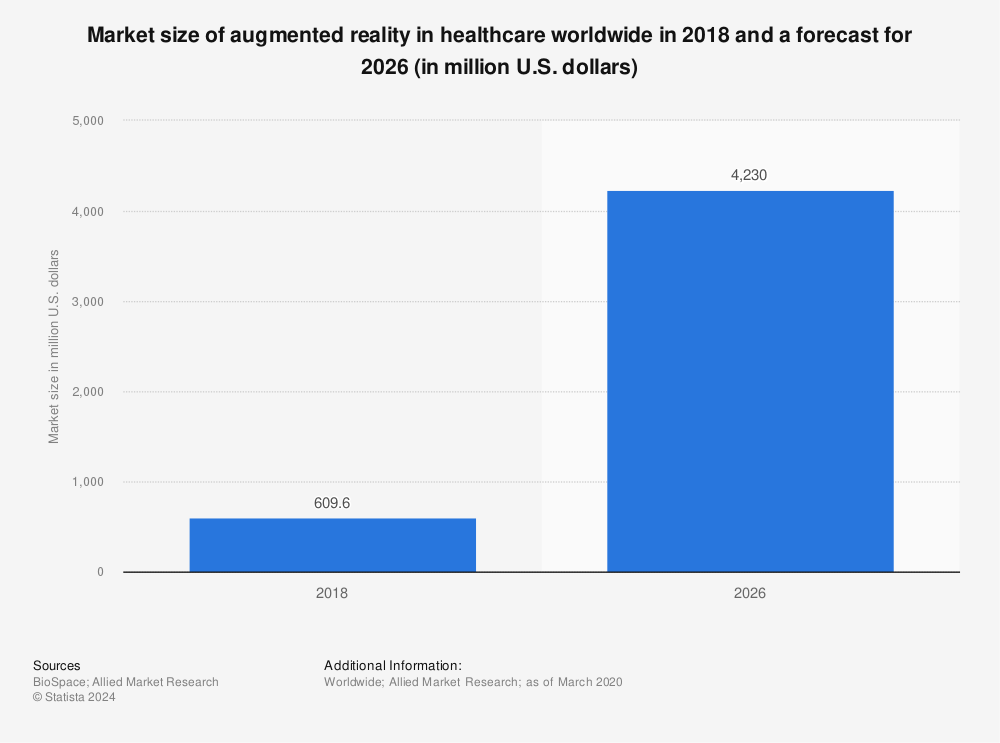
Find more statistics at Statista
ResearchAndMarkets predicts that the global augmented reality market will be around $152 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36%, while the global augmented reality healthcare market will grow at a CAGR of 26%. (2022-2027).
What is AR & VR ?

Reality technologies such as Augmented reality(AR) and Virtual reality (VR) supplement or entirely replace the user’s actual surroundings.
- AR technology uses a device’s camera to superimpose computer-generated imagery (CAI) onto a user’s real-world perspective.
- VR allows users to have an experience that is indistinguishable from being in a real-life setting.
With AR, a computer-generated simulation is superimposed over the user’s view of the physical world to provide contextual information and insights. When a user points their phone’s camera to a piece of malfunctioning machinery, for instance, an augmented reality software designed for the industrial sector may immediately display troubleshooting advice.
A user’s real-world surroundings are fully simulated in a virtual reality experience. Since everything in these worlds is made up, they are usually blown out of proportion. A user of virtual reality technology may, for instance, enter the ring with a cartoon rendition of boxing legend Mike Tyson.
While the goal of both virtual and augmented reality is to place the user in a simulated environment, the two concepts are distinct and have different applications.
Our experts can help you in developing your world-class AR/VR Applications..
What is the Future of AR and VR in Healthcare?
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are still in their infancy but are already beginning to alter the healthcare industry. Three years from now, there may be as many as 30 million people using these technologies; six years from now, that number might rise to 70 million. AR and VR will be employed in many different fields of healthcare, from rehabilitation after a stroke or loss of vision to stress management, exercise, and speech therapy, saving countless hours for healthcare workers and saving the lives of their patients.
Five major developments in the field of virtual reality are as follows:
More Access to Health Information
Wearing a set of augmented reality (AR) glasses will be the first thing patients do when they visit a doctor in the future, giving them instant access to data visualizations, charts, and other helpful visual aids during their consultations. A more enlightening and thorough learning experience is guaranteed to occur from this appointment.
Medical Education and Practice
Virtual reality (VR) technology is widely expected to play a significant role in most future surgical training protocols, allowing students to polish their skills on lifelike simulated patients. The training is superior to traditional cadaver practice because it gives surgeons a more realistic experience and a wider range of anatomical structures to learn about and work with.
Breakthroughs in Physical Rehab
As Allure’s usage of Jentronix demonstrates, VR has the potential to transform the field of physical rehabilitation completely, and AR is not far behind. Patients undergoing physical therapy will soon be able to wear augmented reality glasses while wired up to electrodes. The patient’s ability to monitor their vital signs during physical therapy (including heart rate, blood pressure, calorie burn, flex strength, and other metrics) is a major step toward improving outcomes from treatment.
Superior Quality of Care in Remote Locations
Patients with long-term health problems will soon be able to receive in-home care using augmented and virtual reality technologies. Those unable to move around or be carried out easily would appreciate this. With the help of such gadgets, a healthcare provider in another location can connect with a patient in their own home and provide thorough consultations and detailed demonstrations without ever having to meet in person.
Instructional Videos for Patients
Patients will soon be able to see exactly what their surgeries will look like rather than relying on their imaginations. With the mobile app development of VR technology, surgeons can pre-surgery brief their patients. Knowing this will help patients feel much less anxious.
Our experts can help you in developing your world-class AR/VR Applications..
How Is AR and VR Used in Healthcare?
Virtual reality (VR) is quickly becoming one of the 21st century’s crucial technologies for efficient healthcare, although few people outside the medical industry know this. It is thrilling because virtual reality could help in ways that conventional medicine cannot.
Here, we will examine the many applications of VR/AR in healthcare and discuss how they are helping both patients and doctors.
Treatment for unique Patients
Medical professionals used a VR interface with imaging software to devise a novel operation for a baby born with a potentially fatal cardiac defect. This use of VR has attracted significant media attention.
Virtual reality (VR) is a remarkable tool for treating individual patients. Since VR representations of key anatomical sections may be produced using compilations of data that healthcare workers already obtain. Therefore, utilizing data collected from MRIs and other imaging technologies, clinicians can construct 3D representations of problem locations.
Suppose doctors have access to the correct VR technology and the ability to utilize it to aid uncommon patients. In that case, they will be able to save many lives by using 3D models without opening the patient in the operating room to look at what there is to work with.
In addition, imaging and 3D modelling advancements will aid clinicians by allowing them to map patient traits onto quantitative rubrics to determine the appropriate course of action.
Treating Patients with Irresistible Symptoms
Preliminary cases suggest that VR can help alleviate the symptoms of poor balance in many medical diseases involving the brain or the inner ear, where it is notoriously difficult to treat.
The concept is that doctors can learn more about their patient’s problems by observing them while they interact with virtual worlds under their control. Then use that information to design treatments that will be most effective for them. To date, there has been no documented case of complete symptom remission due to virtual reality. Nevertheless, researchers and medical professionals are just getting started in this field.
Inducing Patient Distraction During Procedures
Virtual reality (VR) can be a helpful distraction for patients undergoing painful or unsettling medical procedures while awake.
Doctors are considering VR pain management in addition to painkillers to treat patients with serious burns. Changing the dressings on burn sufferers is a particularly unpleasant process. Since burn wounds are so severe and the pain is resistant to traditional painkillers.
VR software named “Snow World” was developed to help burn patients relax and feel less pain during bandage changes. Patients who used Snow World reported almost half as much agony as those who did not; once these findings are clinically validated, every burn unit should have a VR headset.
Virtual reality (VR) can distract patients from the discomfort of medical procedures and potentially mask the unsettling sounds that certain of these treatments might cause.
Care for Psychological Disorders
Since many mental illnesses are difficult to treat, there has been a lot of interest in virtual reality (VR) as a potential therapeutic method. Clinicians have been working hard to incorporate VR into areas like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) with promising results.
Using VR to desensitize phobic patients by systematic exposure to the object of their phobia in a virtual world also shows great promise. Doctors may have patients deal with their phobia safely before sending them into real-world desensitization.
Educating Future Health Care Workers
One of the most promising applications of VR is in the education of future physicians. Training doctors, nurses, and specialists like surgeons takes an enormous amount of time.
Virtual reality (VR) can be the best tool for bridging the gap between medical school and the operating room. VR provides more realistic teaching environment to healthcare workers. Future haptic feedback technology will allow doctors to receive physical input during virtual reality practice sessions. It enhance their capacity to provide care.
Virtual reality (VR) has the potential to give a medical school education at a fraction of the present cost. The public will have easier access to the knowledge and wisdom of doctors because of this.
The Use of Virtual Reality in Healthcare
Despite how spectacular it may seem now; virtual reality remains a developing technology. There will undoubtedly be further astonishing breakthroughs. Carrie Shaw is of the opinion that her company has barely scratched the surface of virtual reality.
She estimated they used about 5% of the hardware’s potential. Everything from the way it was filmed to the ability to incorporate branching plots and have artificial intelligence react to your actions.
Carrie Shaw remarked, “There’s a lot of talk about virtual reality and how it may be used as an empathy machine.” We discuss it like it is a movie or a game, but it is quite scientific. Empathy is more than a warm fuzzy sensation; it is a tool for learning and changing attitudes and actions.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, VR is transforming healthcare in a way that yields better outcomes for patients. It boosts the efficiency of doctors, and enables doctors to treat previously unreachable patients and symptoms.
The need for healthcare-specific virtual reality headsets is now hampering the widespread use of this technology. Healthcare organizations worldwide will be vying for a piece of the action as soon as one inventive hardware firm takes on the challenge of developing virtual reality headgear that is hygienic and tailored to the needs of the healthcare industry.
The advancement of VR-aiding technologies like haptic feedback and robotics will lead to a rise in the healthcare sector.
JumpGrowth’s goal is to corner the market globally with the AR VR app development solution supplier. With innovative AR VR Development services, we provide a wide variety of services for the healthcare sector.
Our experts can help you in developing your world-class AR/VR Applications..